The role of the Amygdala

The Brain's Fear Engine: Exploring the Amygdala's Role
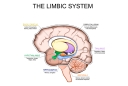
The amygdala, a pair of almond-shaped clusters deep within the temporal lobe of the brain, is a critical component of the limbic system—a network responsible for regulating emotions, memory, and survival instincts. Though small in size, the amygdala wields immense power, acting as the brain's emotional command center.
Often dubbed the "fear center", the amygdala is best known for its role in processing fear and triggering the "fight or flight" response when danger is detected. However, this nickname oversimplifies its capabilities.
Beyond fear, the amygdala is also essential for understanding emotional nuances, forming memories, guiding social behavior, and even influencing decision-making and motivation. Understanding the amygdala isn't just about appreciating its biological function—it's about recognizing its impact on everyday life. From managing anxiety to building emotional resilience, the amygdala plays a pivotal role in mental health.
Anatomy of the Amygdala
The amygdala is a small but powerful structure nestled deep within the brain's , forming an integral part of the limbic system—a network responsible for emotions, memory, and behavior.
It consists of multiple clusters with distinct roles in processing emotions and connecting it to other parts of the brain.
Though compact, the amygdala's strategic location and connections make it a central hub for processing emotions and coordinating the brain's survival mechanisms.
How the Amygdala Processes Fear
This serves as the brain's early warning system, constantly scanning the environment for threats. When a potential danger is detected - be it a shadowy figure in a dark alley or a sudden loud noise - the amygdala processes this information and triggers the "fight or flight" response.
| Fight Reaction | Flight Reaction |
|---|---|
| Confronting the perceived threat head-on. | Escaping or avoiding the perceived threat. |
| Aggressive or defensive actions (e.g., shouting, attacking). | Evasive actions (e.g., running away, hiding) |
| Fighting off an attacker to protect oneself | Running from a dangerous animal or a burning building. |
The amygdala identifies threats by receiving sensory information from the environment via the thalamus and comparing it to stored emotional memories in the hippocampus. If the situation is deemed dangerous, the amygdala sends signals to the hypothalamus, activating the sympathetic nervous system. This cascade results in physiological changes such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened alertness, all designed to prepare the body for action.

A threat is perceived. The thalamus communicates with the amygdala. Triggering a fear response. The sympathetic nervous system is activated - intiating a "flight or fight" reaction. The hippocampus stores the fearful event for future reference. Description adapted from www.simplypsychology.org/amygdala.html
Beyond Fear: The Multifaceted Amygdala
While it's most renowned for its role in fear, its influence extends far beyond that, affecting multiple aspects of our emotional and social lives.
- Emotional Processing When we encounter a situation, the amygdala evaluates it in real-time, quickly determining whether it carries positive, negative, or neutral emotional weight. It is involved in interpreting facial expressions, vocal tones, and other subtle cues, shaping our emotional responses. This process ensures that emotionally charged memories, whether joyous or distressing, are prioritized and encoded in the brain, making these events more vivid and lasting.
- Memory and Learning While the hippocampus is responsible for forming new memories, the amygdala ensures that those memories tied to strong emotions are especially memorable. This collaboration is essential for fear conditioning, where emotionally significant events (e.g., traumatic experiences) are stored and learned for future reference. In this way, the amygdala helps us learn from past emotional experiences, shaping behavior and decision-making based on previous outcomes.
- Social Behavior The amygdala also plays a vital role in recognizing emotions in others, which is fundamental for successful social interactions. It helps us identify subtle cues like facial expressions, body language, and even vocal tones, allowing us to interpret whether someone is happy, sad, angry, or fearful.
- Reward and Motivation Beyond fear, the amygdala is deeply involved in reward-based learning and motivation. It associates certain actions or experiences with emotional rewards (such as pleasure or satisfaction), reinforcing behaviors that promote survival or pleasure.
Small But Powerful
The amygdala, though small in size, holds an outsized influence over our emotions, behaviors, and survival instincts. From orchestrating the fear response to shaping emotional memories, guiding social interactions, and influencing motivation, this almond-shaped structure is a cornerstone of the brain's emotional and behavioral systems.
As research progresses, the implications of understanding the amygdala extend far beyond neuroscience. By exploring how this powerful structure interacts with other parts of the brain, we can develop more effective therapies, from targeted medications to brain-stimulation techniques, to help people regain control over their emotions.
In many ways, the amygdala reflects the duality of human emotion—its ability to protect us through fear and enrich our lives through emotional depth. By unraveling the mysteries of this remarkable structure, future research holds the promise of transforming the way we manage mental health challenges, offering new hope for emotional resilience and well-being.
SEARCH ARTICLES
advanced search tips examples: "Yoga Meditation" Therap* +Yoga +MeditationRecent Posts

Mar 09 2026
The Biological Drive to Play

Nov 27 2025
The Psychology Behind the Primacy Effect

Jun 24 2025
Microplastic Exposure: Bottled Water vs Tap

Jun 09 2025
Squats for aligning hips

Apr 29 2025
Creative Thinking

Jan 28 2025
How to talk to someone you disagree with

Jan 27 2025
Alcohol Causes Cancer
Jan 14 2025
The role of the Amygdala

Oct 04 2024
A Support Guide for Anorexia Nervosa



